Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-26 Origin: Site








Building a 5 axis CNC router is one of the most ambitious engineering projects for designers, makers, manufacturing engineers, and companies seeking high-precision machining capabilities. Unlike basic 3-axis systems, a 5-axis machine offers full rotational freedom and the ability to cut from virtually any angle. This dramatically expands its applications in aerospace, automotive, molds, composites, aluminum machining, and advanced prototyping.
However, designing and constructing a high-performing 5-axis CNC router from scratch requires deep mechanical understanding, precise planning, and proper execution. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of how a multi-axis machine works, essential components, step-by-step building instructions, and performance-optimization tips. Whether you are a DIY builder, an engineering student, or a manufacturer evaluating whether to build or buy a 5 axis CNC router machine, this guide will give you clarity.
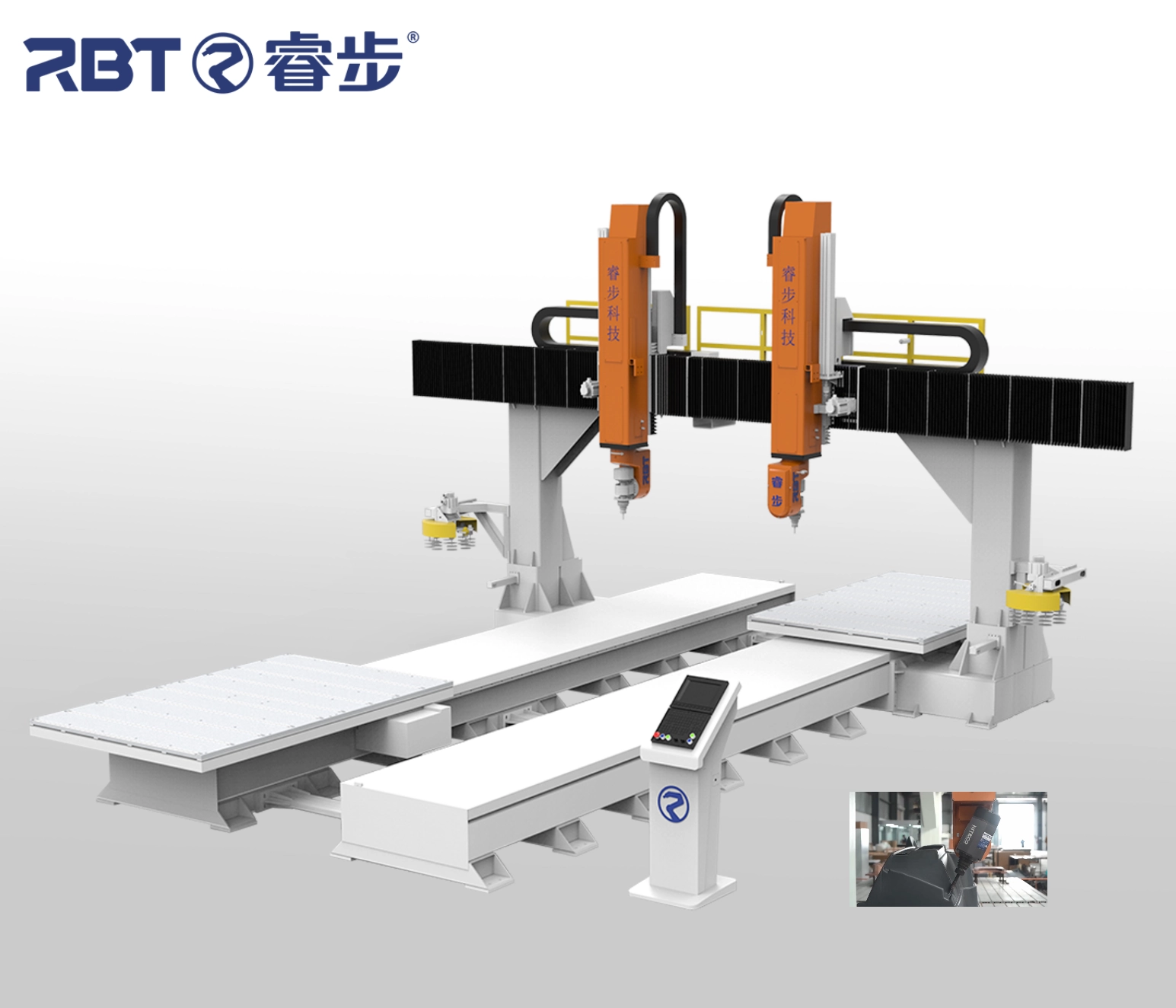

A 5 axis CNC router is a computer-controlled cutting machine capable of movement on three linear axes (X, Y, Z) plus two additional rotational axes (A, B or A, C). This allows the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from any direction.
A 3-axis CNC can cut flat surfaces and simple contours, but it struggles with:
Undercuts
Deep cavities
Multi-sided machining
Complex 3D surfaces
A 5 axis CNC routing machine can rotate either the tool or the table, enabling the machining of complicated geometries in a single setup. This improves accuracy, reduces cycle time, and eliminates repositioning.
Short answer: yes.
But it requires:
Strong mechanical knowledge
Access to machining tools
Precision components
CAD/CAM software
Proper calibration techniques
Building a 5-axis machine is significantly more challenging than assembling a 5 axis CNC router kit, because of the complexity of kinematic motion, rigidity requirements, and control systems involved.
This guide shows the full process.
Before sourcing materials, you must define the goals and limitations of your machine.
What materials will you cut?
(Plastic, wood, composites, aluminum, foam, etc.)
What working area size do you need?
How rigid must the structure be?
Should the additional axes rotate the spindle or the table?
What accuracy and feed rate do you require?
What is your realistic budget?
A 5-axis CNC router machine designed for cutting aluminum, for example, needs much greater rigidity than one used for foam or composite trimming.
There are three dominant designs:
Large working area
Good for plastics, composites, and molds
Common in thermoforming trimming
Table rotates (A/C)
Higher rigidity
Suitable for small precision parts
Spindle rotates on A and B axes
Excellent for freeform surfaces
Used in aerospace and automotive styling
Choosing your structure is essential before beginning design.
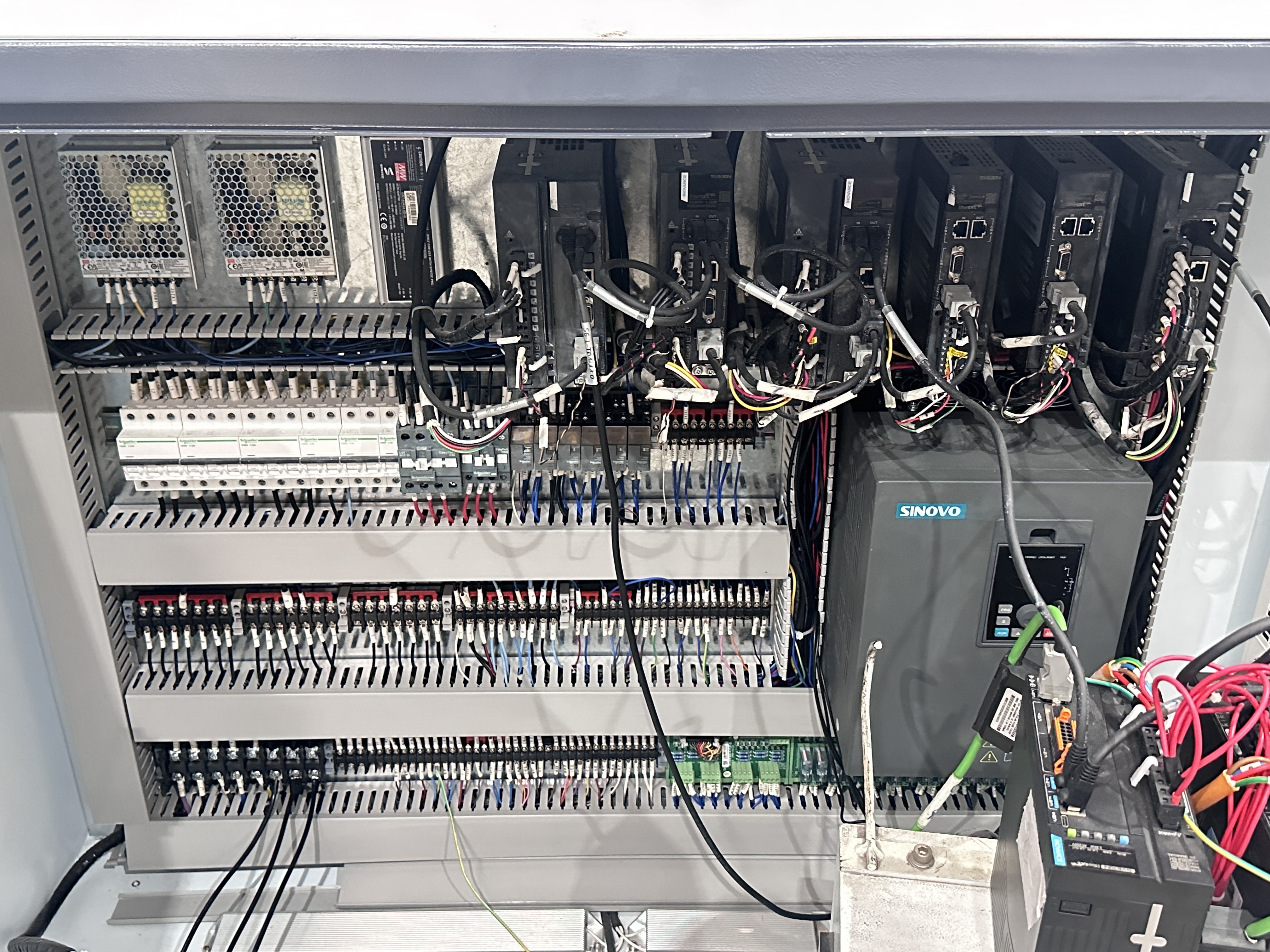
Constructing the machine requires advanced mechanical and electrical components. Below is a detailed breakdown.
The frame supports the entire machine. It must be:
Rigid
Vibration-resistant
Precision welded or cast
Common materials:
Steel (for rigidity)
Aluminum (for lightweight designs)
High-quality motion components ensure accuracy:
Linear guide rails
Ball screws
Rack & pinion modules
Precision bearings
A 5-axis system includes:
Rotation around the X-axis.
Can be implemented through:
Rotary tables
Swivel heads
Tilting fixtures
Allows rotation around Z or Y.
Essential for multi-directional cutting.
These axes require high-precision harmonic drives or planetary reducers to maintain accuracy under load.
You must choose a spindle based on your cutting application:
2.2 kW spindle for wood/plastics
6–10 kW spindle for composites
12 kW spindle for aluminum machining
Important spindle attributes:
RPM range
Torque curve
Tool holder type (ER collet / ISO / HSK)
Air-cooling or water-cooling
A robust controller is necessary for coordinated 5-axis movement:
Siemens
Fanuc
Syntec
Mach4 (DIY kit level)
LinuxCNC (open-source)
More advanced controllers offer smoother motion, better interpolation, and improved surface finish.
To operate a 5-axis CNC machine, you need:
CAD software (SolidWorks, Fusion 360, Catia)
CAM software that supports 5-axis toolpaths
(HyperMill, Mastercam, PowerMill, Fusion 360 Ultimate)
Post-processor for your specific controller
Software compatibility is crucial in multi-axis systems.
Below is a practical guide outlining each stage.
Start by modeling:
Frame
Gantry
Linear rails
Rotational axes
Spindle head
Electrical cabinet
Simulate the machine’s movement to detect collisions or weak points.
Precision is essential.
Ensure:
Welds are clean
Straightness is within tolerance
Surfaces are machined flat
Anchoring is stable
A rigid frame eliminates vibrations and increases machining accuracy.
Mount rails on machined surfaces.
Ensure:
Perfect alignment
No backlash in ball screws
Light but consistent preload
This guarantees smooth, accurate motion.
This is the most complex part of the build.
For rotational axes:
Use high-precision harmonic drives
Minimize backlash
Use absolute encoders for accuracy
Ensure smooth rotation under load
Test rotational movements thoroughly.
Align the spindle with:
Z-axis bearings
Tool center point calibration
Proper torque mountings
Ensure adequate cooling and safety shields.
Inside the electrical cabinet:
Install servo drivers
Route cables cleanly
Use shielding to avoid electrical noise
Add limit switches
Install the controller and interface
Test all axis movements at low speed first.
Load your:
CAM profile
Controller configuration
5-axis post-processor
Calibrate:
Tool offsets
Rotational center points
Work coordinate systems
Kinematics
This is essential for accurate 5 axis CNC routing.
Perform:
Axis homing
Backlash testing
Accuracy verification with dial indicators
Material cutting trials
Refine acceleration curves and feed rates.
Using a weak frame causes vibration errors
Poor spindle selection limits cutting capability
Incorrect rotational axis alignment leads to tool path errors
Using low-grade rails reduces accuracy
Skipping kinematic calibration ruins 3D surface finish
Undertsizing servo motors reduces speed and torque
A 5-axis CNC router machine is only as strong as its weakest component.
Building your own machine is educational and rewarding, but:
Requires months of work
Needs access to machining tools
Needs expert calibration
May lack commercial precision and reliability
Buying a professionally engineered 5-axis CNC router provides:
Industrial accuracy
Faster production
Advanced control systems
Warranty and long-term support
Stable structure and tested kinematics
CNC-optimized components
Many companies eventually choose professional machines for consistent production.
A well-built machine can perform:
Mold machining
Composite trimming
Thermoformed plastic cutting
Aluminum milling
Marine and aerospace component machining
3D surface sculpting
Automotive interior and exterior trimming
Carbon fiber product drilling and contouring
This is why industries worldwide rely on 5-axis technology.
Keep the frame as rigid as possible
Upgrade to better servo motors
Choose premium guide rails
Add harmonic reducers for rotational axes
Enable advanced CAM smoothing algorithms
Use high-quality tooling
Implement vibration damping
Add dust extraction and cooling systems
These upgrades significantly improve surface quality.
Building a 5 axis CNC router on your own is absolutely achievable, but achieving industrial-level precision and stability requires extensive engineering experience, advanced components, and professional calibration. If your goal is stable mass production, high-accuracy mold machining, composite trimming, or aluminum cutting, investing in a professional multi-axis machine will dramatically improve your manufacturing performance.
Fujian RBT Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd.is a leading multi-axis CNC machine manufacturer with 24+ years of experience. We specialize in professional 5-axis CNC routers, gantry machining centers, composite trimming routers, and customized multi-axis systems. With global service coverage, strong R&D capability, and high-precision manufacturing, RBT provides reliable, efficient, and cost-effective CNC solutions for customers worldwide. If you want assured quality, performance, and long-term support, RBT is your ideal partner.
1. Is it difficult to build a 5-axis CNC router?
Yes. The mechanical and control complexity is much higher than a 3-axis system. It requires precise alignment, calibration, and high-quality components.
2. What materials can a 5-axis CNC router cut?
Composites, plastics, foam, wood, aluminum, copper, and other soft metals depending on spindle power and machine rigidity.
3. How accurate is a DIY 5-axis CNC router?
Accuracy varies widely. Professional machines can reach ±0.02 mm or better, while DIY machines may achieve ±0.1–0.3 mm depending on build quality.
4. Should I buy a 5-axis CNC router kit instead of building from scratch?
A 5 axis CNC router kit simplifies assembly and reduces design errors, but still requires calibration and tuning. It’s a good middle-ground option.
5. Why do industrial companies prefer commercial 5-axis CNC routers?
Because commercial machines offer proven rigidity, certified accuracy, reliable components, software integration, and long-term after-sales support—critical for production environments.